Since then, as it became clear that the computer does not need to occupy an entire room, is quite enough and the usual table, users of these computing devices have begun to dream of "a computer in your pocket." Personal computers are gradually reduced their size and variety of forms. Emerged a class of devices like laptop, the first publicly available model was released in 1981, at a certain fitness it could even carry - weight "machine" was 11 kg. The concept of a handheld computer came much later and was originally proposed for devices that actually perform the functions of the organizer. Now the worlds PCs and PDAs is gradually moving to meet each other - PDAs are becoming more powerful and more functional, and PC all portable and suitable for use in mobile environments. Last spring, at the CeBIT trade show it seemed that there was a real breakthrough - was presented to a new class of devices called UMPC - ultra mobile PC. The devices submitted under this name by several manufacturers, were truly portable, runs on Intel Pentium or VIA C7-M, running Windows XP Tablet PC Edition 2005. That is, they were not trimmed to device capabilities, and full-fledged computers that they could have run the usual applications for PC users. Separate attempts to create similar devices made before, but they had several shortcomings, which could resist the UMPC, chief among them - the high cost. If predecessors in most UMPC worth about $ 2 thousand, or even above, the ultra-mobile PCs lowered the bar to about $ 1 thousand, however, has shown almost a year available in the sale of such devices, they were not mobile enough - and too big size and battery life work is low.
 |
Evolution continues, developers are not standing still. Earlier this year, introduced several new UMPC has a wider variety of form factor and a bit more optimistic figures for the duration of the work on a single battery charge (3-4 hours). Whereas in the past year ultra-mobile PCs were similar to twins - a 7-inch screen form factor "monoblock", and now displays, and thus the size range (5-7 inches), also appeared in various configurations mostly play up different ways to integrate QWERTY-keyboard.
 |
 |
 |
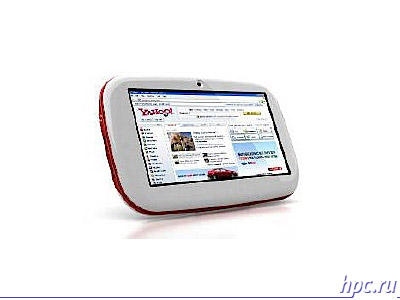
At which started in Beijing Intel Developer Forum theme mobile computers, has not remained unaffected. Plans were announced for the new mobile platform based on the new processors for future generations of laptops, also did not escape the topic and smaller machines, approaching in size to the pocket. Firstly, there is demonstrated a prototype of the next UMPC, which is based on has not yet announced by the processor, operating system Windows Vista.At the same time he is able to work about 4.5 hours in offline mode when using the 3D-interface Vista Aero. Well, a small but still one step ahead. Form factor, however, does not differ is originality, a similar form is used, for example, models of Sony UX.
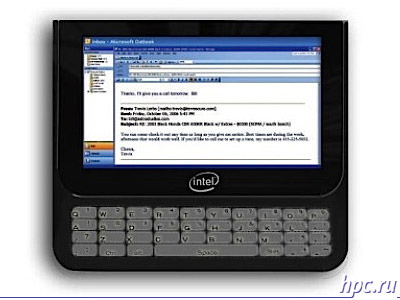
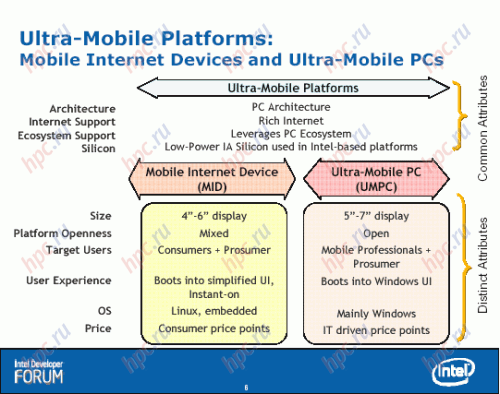
Secondly, Intel introduced yet another, new class of devices - MID (Mobile Internet Device). It is noticeably more "pocket" solution than the classical UMPC. Here is how to divide these two classes of devices itself Intel:
- UMPC are intended primarily for mobile professionals, MID - for consumers and professionals
- UMPC equipped with a display diagonal of 5.7 inches, and MID - 4 - 6 inches
- UMPC has a user interface, Windows, and MID - simplified interface
- Finally, one of the major differences - MID will work based on Linux!
 |
 |
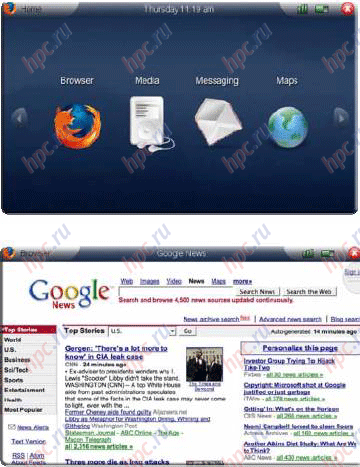
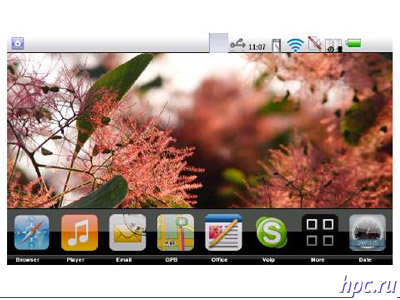
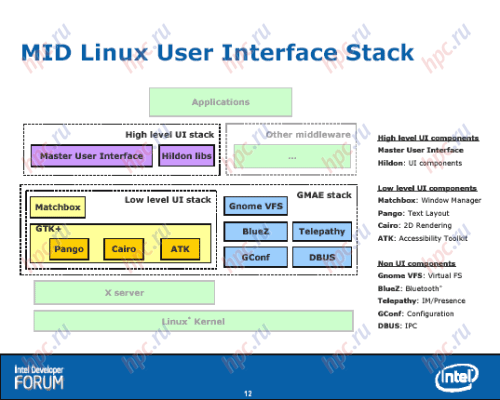
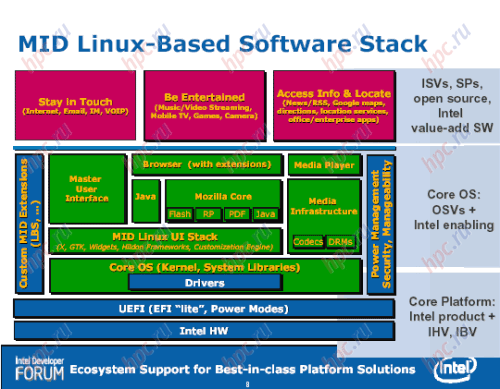
MID interface deserves special attention. It was created with a focus on managing your fingers across the touch screen. The organization and design in some places, like the phone interface iPhone, which gradually becomes a model of governance with a finger. Judging by the documents submitted, the first mobile device in this class will work on the basis of the so-called RedFlag MIDInux, first adapted to the MID distro Linux. It is based on the kernel Linux 2.6.20. It is expected that the first version of RedFlag MIDInux will be available in May. The system works well with 256 MB RAM, adapted to the small screen with a resolution of 800x480 pixels or 1024x600 pixels. Potentially supported by the cellular network (WWAN), WLAN, interface Bluetooth, USB (client), GPS, mobile TV and the like.
 |
 |
 |
 |
Now the company has introduced several designs of such devices. One of them - intended primarily for entertainment. The device must have a 5.4 inch display, weigh less than 300 grams. Has built-in camera, quick access to control music playback, as well as for games.Supports mobile TV, user interface Bluetooth, including listening to music.
The main task of the other - fast access to information and location-based services. The device is equipped with a 5-inch display, has extensive communications capabilities, equipped with GPS-module and FM-tuner. Among other things - working with the services Push e-mail.
Information on other design options while there is little, but you can see the image. For example, this version is designed for fans of instant messaging.
According to the company's plans in 2008 for such devices will be significantly reduced power consumption, size and thickness. This will be achieved by a complex of measures, including work on the parameters of the display and use of drives based on flash memory (SSD) instead of hard drives based on magnetic disks. Projected to Intel, by 2010 MID market will be about 180 million devices. However, there remain many gaps with respect to performance. It is not known which specific processors will operate the device in one document only mentioned the Intel chipset 915. In any case, it is clear that Intel will do its utmost to promote and support this project, and support for such a giant is worth a lot. Let's wait for the details and see what the future will show:) The authors, translation: